Leetcode 236 Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree
Leetcode 236 Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree
Problem description
Given a binary tree, find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree.
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes p and q as the lowest node in T that has both p and q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).”
Example 1:
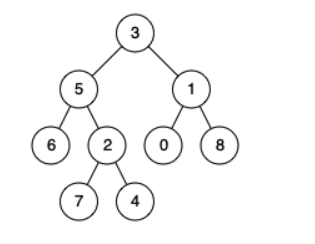
- Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
- Output: 3
- Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 1 is 3.
Example 2:
- Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4
- Output: 5
- Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 4 is 5, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
Example 3:
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [2, 105].
- -10^9 <= Node.val <= 10^9
- All Node.val are unique.
p!=qpandqwill exist in the tree.
Process
Let lca_node be the lowest common ancestor of nodes p and q. Then lca_node must satisfy one of the following:
pandqare in the left and right subtrees oflca_node, respectively.p == lca_node, andqis in either the left or right subtree oflca_node.q == lca_node, andpis in either the left or right subtree oflca_node.
To find lca_node recursively, the following conditions should be met:
- If both
pandqare not null, return their common ancestor. - If only one of
porqexists, return the one that exists. - If neither
pnorqexists, returnNone.
Detailed Algorithm
If the current node
nodeequalsporq, thennodeis the lowest common ancestor ofpandq.
→ Returnnode.- If the current node
nodeis not null, recursively search both left and right subtrees:- If both left and right subtree results are not null, it means
pandqare on different sides, and the currentnodeis their LCA.
→ Returnnode. - If the left subtree is null, return the result from the right subtree.
- If the right subtree is null, return the result from the left subtree.
- If both are null, return
None.
- If both left and right subtree results are not null, it means
- If the current node
nodeisNone, then neitherpnorqare in this subtree.
→ ReturnNone.
Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':
if root == p or root == q:
return root
if root:
node_left = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
node_right = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
if node_left and node_right:
return root
elif not node_left:
return node_right
else:
return node_left
return None
Time complexity and space complexity
- Time complexity:\(O(n)\),where \(n\) is number of node of tree。
- Space complexity:\(O(n)\)。
Reference
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.